1N4001 vs 1N4007: What are Differences and How to Choose
 Published: Sep 11, 2023
Published: Sep 11, 2023
Contents
When it comes to diodes, the 1N4001 and 1N4007 are two commonly encountered components in the world of electronics. The 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes are both members of the 1N400x series and share many similarities in terms of their function and basic specifications.

In this article, we will explore the distinctions between the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes, helping you understand their unique characteristics and guiding you in making the right choice for your specific applications.
Question from Quora: Can I use 1N4007 instead of 1N4001?
Yes, you can generally use a 1N4007 diode in place of a 1N4001 diode in most applications without any issues. The main difference between these two diodes is their voltage and current ratings.
The 1N4001 is rated for a maximum voltage of 50 volts and a current of 1 ampere. On the other hand, the 1N4007 has a higher voltage rating of 1000 volts and a current rating of 1 ampere. The 1N4007 is essentially a higher voltage version of the 1N4001, but it can still be used at lower voltages and currents without any problems.
So, if you have a 1N4007 and you need to replace a 1N4001 in your circuit, it should work just fine. However, keep in mind that the 1N4007 may be physically larger than the 1N4001 due to its higher voltage rating, so you'll need to make sure it fits in your circuit board or enclosure.
Part 1. What is 1N4001
1. 1N4001 Overview
The 1N4001 is a popular and widely used semiconductor diode, specifically a rectifier diode. It is part of a family of rectifier diodes known as the 1N400x series, where "x" can vary to denote different voltage ratings. The "1N4001" specifically refers to a diode with a 1-ampere (A) current rating and a voltage rating of 50 volts.
2. 1N4001 Pinout

1N4001 Pinout
|
Pin No. |
Pin Name |
Current Flow Direction |
|
1 |
Anode |
Current always enters through Anode |
|
2 |
Cathode |
Current always exits through Cathode |
3. 1N4001 Features
Specifications
- Average Forward Current: 1A
- Non-Repetitive Peak Current: 30A
- Reverse Current (Leakage Current): 5μA (microamperes)
- RMS Reverse Voltage: 35V (Root Mean Square)
- Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage: 50V
- Package Type: DO-41
Features
- Rectification: The primary function of the 1N4001 diode is rectification, converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing current flow in one direction only.
- Current Rating: It has a current rating of 1 ampere (A), which means it can handle a maximum continuous forward current of 1A without breaking down.
- Voltage Rating: The diode is rated for a maximum reverse voltage of 50 volts (V), meaning it can withstand up to 50V in the reverse-bias direction without breakdown.
- Fast Recovery Time: The 1N4001 has a relatively fast recovery time, making it suitable for applications that require switching between forward and reverse bias.
- Standard Package: It typically comes in a cylindrical glass or plastic package with two leads (anode and cathode), making it easy to integrate into various electronic circuits.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: It exhibits a relatively low forward voltage drop, typically around 0.7 volts (V), which helps minimize power loss when conducting current.
- Rugged and Reliable: The 1N4001 is known for its robustness and reliability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Reverse Polarity Protection: It is commonly used to provide reverse polarity protection in electronic circuits, preventing damage due to incorrect power supply connections.
- Cost-Effective: This diode is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for basic rectification and protection tasks.
- Temperature Range: It can operate within a temperature range typically from -65°C to +175°C, depending on the specific manufacturer's datasheet.
- Widespread Availability: Due to its popularity and usefulness, the 1N4001 diode is widely available from various semiconductor manufacturers.
4. 1N4001 Application
- Reverse Polarity Protection: It can be used to prevent damage due to reverse polarity connections in electronic circuits.
- Rectification in Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers: It's commonly used in both half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits to convert AC voltage to DC voltage.
- Protection Device: It serves as a protective component in circuits to prevent voltage spikes and reverse current flow.
- Current Flow Regulation: It can act as a simple current flow regulator or limiter in certain circuits.
5. 1N4001 Equivalent
The replacements for the 1N4001 diode are 1N4733A,1N4148, 1N5822, 1N5408, and Zener Diodes.
6. 1N4001 Datasheet PDF
Check and download 1N4001 datasheet PDF here>>
7. 1N4001 Manufacturer
The 1N4001 diode is commonly manufactured by "Diodes Incorporated." Diodes Incorporated is a well-known semiconductor manufacturer that produces a wide range of diodes and other semiconductor components. The 1N4001 is part of their product lineup and is widely used in various electronic applications, including rectification in power supplies, reverse voltage protection, and signal clipping.
Diodes Incorporated is known for producing high-quality components, and their 1N4001 diode is a popular choice in the electronics industry for its reliability and performance. If you are looking for the 1N4001 diode, you can find it under the brand name "Diodes" or "Diodes Incorporated" from various distributors and suppliers.
Part 2. What is 1N4007
1. 1N4007 Overview
The 1N4007 is a standard silicon rectifier diode with a 1A forward current rating, 1000V reverse voltage rating, and around 0.7V forward voltage drop, commonly used for converting AC to DC in electronic circuits.
2. 1N4007 Pinout
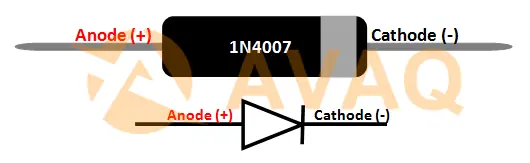
1N4007 Pinout
|
Pin Number |
Pin Name |
Description |
|
1 |
Anode (A) |
The positive terminal where current enters |
|
2 |
Cathode (K) |
The negative terminal with a band or stripe indicating polarity and where current exits |
3. 1N4007 Features
Specifications
- Operating Junction Temperature Range: -55°C to 175°C
- Forward Voltage: 1.1 Volts
- Average Forward Current Rating: 1A
- Non-repetitive Peak Current Rating: 30A
- Reverse Current (Leakage Current): 5µA
- Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage: 1000V
- Power Dissipation: 3W
- Package Type: DO-41
Features
- Rectification: Designed for rectifying alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), making it crucial for converting AC voltage to usable DC voltage.
- High Voltage Rating: Offers a peak repetitive reverse voltage (PRV) of 1000 volts (1kV), making it suitable for handling high-voltage applications.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: Has a low forward voltage drop of approximately 1.1 volts, which minimizes power loss when conducting current in the forward direction.
- High Forward Current: Rated for an average forward current (IF) of 1A, making it suitable for moderate current applications.
- Non-Repetitive Peak Current: Can handle non-repetitive peak currents of up to 30A, allowing it to withstand short-duration overcurrent conditions.
- Low Reverse Leakage Current: Exhibits a low reverse current (leakage current) of only 5µA, ensuring efficient blocking of reverse voltage.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: Operates reliably within a temperature range of -55°C to 175°C, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
4. 1N4007 Application
- Power Supply Rectification: Converting AC to DC in power supplies.
- Voltage Protection: Preventing reverse voltage or spikes from damaging components.
- Battery Charging: Converting AC to DC for charging batteries.
- Signal Clipping: Limiting signal voltages in audio and RF circuits.
- Voltage Multipliers: In voltage multiplier circuits.
- Motor Control: Suppressing inductive kickback in motor control.
- LED Protection: Protecting LEDs from reverse current.
- General Rectification: In various applications requiring AC-to-DC conversion.
5. 1N4007 Equivalent
1N5408, BA159, STTH110
6. 1N4007 Datasheet PDF
Check and download 1N4007 Datasheet PDF here>>
7. 1N4007 Manufacturer
Diodes Incorporated, a prominent semiconductor manufacturer, is known for producing the 1N4007 rectifier diode along with a wide range of electronic components. With a global presence and a reputation for quality and reliability, Diodes Incorporated serves various industries, offering essential solutions for electronic circuitry needs.
Part 3. 1N4001 vs 1N4007: What are Differences and How to Choose
1. What are the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes?
The 1N4001 and 1N4007 are both types of rectifier diodes. They are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction, making them suitable for converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in electronic circuits.
2. What is the main difference between the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes?
|
Characteristic |
1N4001 |
1N4007 |
|
Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage |
50V |
1000V |
|
Average Forward Current Rating |
1.0A |
1.0A |
|
Common Applications |
Low-voltage tasks |
High-voltage tasks |
|
Typical Uses |
Low-power rectification |
Power supplies, rectification in high-voltage circuits |
|
Voltage Range |
Suitable for voltages below 50V |
Suitable for voltages up to 1000V |
|
Cost |
Generally more affordable |
Slightly more expensive due to higher voltage rating |
|
Selection Criteria |
For low-voltage applications |
For high-voltage applications or when a higher voltage margin is needed |
3. How to Choose between 1N4001 vs 1N4007
Choosing between the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes depends on your specific circuit requirements.
Step1. Determine Your Voltage Requirements:
Consider the voltage levels in your circuit. If your circuit operates at voltages below 50V, the 1N4001 may be sufficient. For circuits with voltages exceeding 50V, consider the 1N4007.
Step2. Assess Current Needs:
Evaluate the current requirements in your circuit. Both diodes have a 1A average forward current rating, so if your current needs are within this range, either diode will work.
Step3. Consider Safety Margins:
If your circuit experiences voltage spikes or variations, or if you want to ensure a safety margin, it's often a good practice to choose the 1N4007 due to its higher voltage rating (1000V). This provides extra protection against voltage surges.
Step4. Cost Considerations:
Consider your budget. The 1N4001 is typically more cost-effective than the 1N4007. If your application can be adequately served by the 1N4001, it may be a more economical choice.
Step5. Availability:
Check the availability of both diodes from your preferred supplier. Sometimes one diode may be more readily available than the other.
Step6. Application Specifics:
Think about the specific application of the diode in your circuit. If you are designing a power supply or rectification circuit for a high-voltage application, the 1N4007 is a safer choice. For less critical or low-voltage applications, the 1N4001 may suffice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your electronic project. These diodes may look similar, but their voltage and current ratings set them apart, making each suitable for different tasks. The 1N4001 is well-suited for low-voltage and low-current applications, while the 1N4007 shines in higher voltage and current scenarios.
Whether you're building power supplies, rectifiers, or protection circuits, understanding the differences between the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes will enable you to make informed decisions and optimize the performance and reliability of your electronic designs.
 FAQ
FAQ
- Can I use these diodes for high-frequency applications?
- These diodes are typically not suitable for high-frequency applications due to their relatively slow recovery time. For high-frequency applications, you may need specialized diodes designed for fast switching.
- Are the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes polarized?
- Yes, these diodes are polarized, which means they have an anode and a cathode. Current should flow from the anode to the cathode, and they should be connected in the circuit with the correct polarity for proper operation.
- What are the other electrical characteristics of the 1N4001 and 1N4007 diodes?
- Both diodes have similar electrical characteristics aside from their voltage ratings. They typically have a forward voltage drop (VF) of around 0.7 volts when conducting current and a maximum forward current (IF) of 1 ampere.
- Can I use a 1N4007 diode in place of a 1N4001 diode?
- Yes, you can generally use a 1N4007 diode in place of a 1N4001 diode if the voltage ratings are compatible with your application. The 1N4007 is backward compatible with lower voltage applications, but it provides higher voltage tolerance.
1N4001-T In Stock: 6070
 Popular Industry Focus
Popular Industry Focus
Hot Products
-
![DMP510DL-7]()
DMP510DL-7
DIODES
DMP510DL Series 50 V 180 mA P-Channel Enhancement Mode Mosfet - SOT-23-3
-
![ZTX651]()
ZTX651
Diodes Incorporated
Bipolar Transistors - BJT NPN Super E-Line
-
![ZVP0545GTA]()
ZVP0545GTA
Diodes Incorporated
P-Channel 450 V 75mA (Ta) 2W (Ta) Surface Mount SOT-223-3
-
![ZVP2110A]()
ZVP2110A
Diodes Incorporated
Trans MOSFET P-CH 100V 0.23A 3-Pin E-Line
-
![BZX84C12-7-F]()
BZX84C12-7-F
Diodes Incorporated
SOT23 Zener Diode rated for 12V
-
![DMP6110SSS-13]()
DMP6110SSS-13
Diodes Incorporated
P-Channel 60 V 4.5A (Ta) 1.5W (Ta) Surface Mount 8-SO
Related Parts
-
![DSK24]()
DSK24
MDD
Diode 40 V 2A Surface Mount SOD-123FL
-
![1S1588]()
1S1588
Onsemi
Diodes - General Purpose, Power, Switching DISC BY MFG 3/04
-
![STTH60L06W]()
STTH60L06W
ST
Diode 600 V 60A Through Hole DO-247
-
![STTH30R04W]()
STTH30R04W
ST
Diode 400 V 30A Through Hole DO-247
-
![CMDSH-3 TR PBFREE]()
CMDSH-3 TR PBFREE
CENTRAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP
Diode 30 V 100mA Surface Mount SOD-323
-
![SM6T12A]()
SM6T12A
Stmicroelectronics
184A@8/20us 600W 21.7V 11.4V Unidirectional 10.2V SMB(DO-214AA) Electrostatic and Surge Protection (TVS/ESD) ROHS
-
![SM15T18A]()
SM15T18A
ST
1500 W, 15.3 V TVS in SMC
-
![1N4003]()
1N4003
NTE Electronics, Inc
<p>This standard rectifier is designed for general purpose, low power applications.</p>
-
![SZMM3Z3V3ST1G]()
SZMM3Z3V3ST1G
onsemi
ZEN REG Zener Diodes - 0.2W TR
-
![NUP4302MR6T1G]()
NUP4302MR6T1G
Onsemi
Fast Switching Speed: With a response time of 5 nanoseconds (5ns)
-
![12CWQ06FN]()
12CWQ06FN
SMC Diode Solutions
Schottky Diodes & Rectifiers RECOMMENDED ALT 78-VS-12CWQ06FN-M3
-
![BA479G]()
BA479G
VISHAY
Pin Diode, 30V V(BR),
-
![1N5819-E3/54]()
1N5819-E3/54
VISHAY
Schottky Diodes & Rectifiers Vr/40V Io/1A
-
![BYV28-200]()
BYV28-200
VISHAY
Rectifiers
-
![BYG22D-E3/TR]()
BYG22D-E3/TR
Vishay
2A 200V SMA SI-DIODE

 Update Time: Sep 13, 2023 Consumer Electronics
Update Time: Sep 13, 2023 Consumer Electronics