1N4007 vs 1N4148: What are Differences and How to Choose
 Published: Sep 13, 2023
Published: Sep 13, 2023
Contents
When it comes to diodes, the 1N4007 and 1N4148 are two frequently encountered components in the world of electronics. Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow the flow of current in one direction while blocking it in the other, making them essential for tasks like rectification and signal clamping. While both the 1N4007 and 1N4148 serve as diodes, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
In this article, we will explore the differences between the 1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes, helping you understand their unique specifications and guiding you in making informed choices for your electronic projects.
1N4007 vs 1N4148: Definition
IN4007 is a rectifier diode commonly used to convert AC to DC, i.e., in rectifier circuits. With high reverse voltage withstand and current withstand, it is widely used in applications such as power supplies and rectifier bridges, and is capable of handling higher voltages and currents.
IN4148 is a high-speed switching diode for electronic circuits that require fast switching, typically used in high frequency circuits and signal shaping circuits. It has characteristics such as fast recovery time and low forward voltage drop, making it suitable for low current and low voltage applications.

1N4007 vs 1N4148: Pinout
1N4007 Pinout
The 1N4007 is a rectifier diode with one pin designated as the anode (positive terminal) and the other pin as the cathode (negative terminal). In a circuit, current should flow from the anode to the cathode for the diode to function correctly.

Here’s the 1N4007 pinout description,
|
Pin Number |
Description |
|
1 |
Anode (Positive Terminal) |
|
2 |
Cathode (Negative Terminal) |
IN4148 Pinout
The IN4148 diode has two pins, with one designated as the anode (positive terminal) and the other as the cathode (negative terminal). In a circuit, current should flow from the anode to the cathode for the diode to operate as intended.
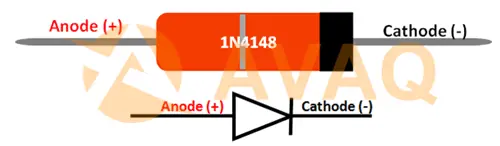
Here’s the IN4148 pinout descriptions,
|
Pin Number |
Description |
|
1 |
Anode (Positive Terminal) |
|
2 |
Cathode (Negative Terminal) |
1N4007 vs 1N4148: Specifications and Features
From here you can check the specifications of 1N4007 vs 1N4148,
|
Specification |
1N4007 |
1N4148 |
|
Type |
Rectifier Diode |
Small-Signal Switching Diode |
|
Peak Reverse Voltage |
1000 volts (1 kV) |
100 volts (0.1 kV) |
|
Average Forward Current |
1 A (1000 mA) |
200 mA (0.2 A) |
|
Peak Forward Surge Current |
30 A |
2 A |
|
Forward Voltage Drop (at 1A) |
Approx. 1 V |
Approx. 0.715 V |
|
Reverse Leakage Current (at 25°C) |
< 5 μA (microamperes) |
< 25 nA (nanoamperes) |
|
Reverse Recovery Time |
Not applicable |
Approx. 4 ns (nanoseconds) |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
-65°C to +175°C |
-65°C to +175°C |
|
Package Type |
DO-41 (Axial Lead) |
DO-35 (Axial Lead) |
|
Common Applications |
Power Supplies, Rectification |
High-Speed Switching, Signal Rectification |
|
Polarity |
Anode (Positive Terminal) and Cathode (Negative Terminal) |
|
1N4007 Features
- Rectification: Converts AC to DC by allowing one-way current flow.
- High Voltage Rating: Handles up to 1000V (1 kV) peak reverse voltage.
- Current Handling: Can manage 1A average current and 30A surge current.
- Low Voltage Drop: Typically has a low 1V forward voltage drop.
- Wide Temperature Range: Operates from -65°C to +175°C.
- Standard Package: Available in a DO-41 package for easy mounting.
- Versatility: Suitable for various general-purpose rectification applications.
- Polarity Markings: Clearly marked anode and cathode for proper orientation.
- Reliable: Known for its consistent and reliable performance.
1N4148 Features
- Fast Switching: Known for rapid switching.
- Low Forward Voltage: Typically 0.715V.
- Small-Signal Diode: For signal applications.
- Peak Reverse Voltage: 100V rating.
- Low Reverse Leakage: Typically < 25nA.
- Quick Recovery: About 4ns.
- Wide Temperature Range: -65°C to +175°C.
- Standard Package: DO-35 for easy installation.
- Versatile: Used in high-frequency and signal circuits.
- Polarity Markings: Clearly marked for correct installation.
- Reliable: Consistent and dependable performance.
1N4007 vs 1N4148: Application
1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes have different characteristics that make them suitable for different applications:
1N4007 Application:
- Rectification: The 1N4007 is primarily used for rectification in power supplies, battery chargers, and other applications where you need to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). Its high voltage and current ratings make it suitable for handling relatively high-power applications.
- High Voltage Applications: Due to its higher peak reverse voltage rating of 1000V, the 1N4007 is well-suited for applications where higher voltage levels need to be rectified.
- General-Purpose Diode: It is commonly used as a general-purpose diode in various circuits that require rectification and voltage conversion.
1N4148 Application:
- Fast Switching: The 1N4148 is known for its fast switching speed and is often used in high-frequency applications where rapid switching of signals is required.
- Signal Processing: It is commonly employed in signal processing circuits, such as amplifiers and oscillators, where its fast recovery time and low forward voltage drop are advantageous.
- Protection Diode: Due to its speed and low voltage drop, it's used as a protection diode in some circuits to prevent reverse voltage or current from damaging sensitive components.
- General Small-Signal Diode: The 1N4148 is a versatile small-signal diode commonly used in a wide range of low-power and signal applications.
1N4007 vs 1N4148: Alternatives
Alternatives to 1N4007 (Rectifier Diode):
1N5408: This is a higher-power rectifier diode with a peak reverse voltage rating of 1000V and a forward current rating of 3A. It can handle higher currents compared to the 1N4007.
1N4004: This is a lower-power alternative with a peak reverse voltage rating of 400V and a forward current rating of 1A. It's suitable for lower-voltage applications.
1N5819: This is a Schottky diode with a lower voltage drop and faster switching characteristics compared to standard rectifier diodes. It's suitable for applications where low forward voltage is critical.
Alternatives to 1N4148 (Small-Signal Diode):
1N4149: This is a higher voltage version of the 1N4148, with a peak reverse voltage rating of 100V. It's suitable for applications that require a slightly higher voltage rating.
1N914: The 1N914 is essentially the same as the 1N4148 and can often be used interchangeably in many applications.
1N5817: This is a Schottky diode with fast switching characteristics and a low forward voltage drop. It's suitable for high-frequency applications and scenarios where low voltage drop is crucial.
1N4001: While it's a rectifier diode like the 1N4007, the 1N4001 has a lower peak reverse voltage rating (50V) and lower forward current (1A). It's suitable for lower-power rectification.
Main Differences Between 1N4007 vs 1N4148
Here are the main differences between 1N4007 and 1N4148,
|
Characteristic |
1N4007 |
1N4148 |
|
Peak Reverse Voltage |
1000V |
100V |
|
Average Forward Current |
1A (1000mA) |
200mA (0.2A) |
|
Peak Forward Surge Current |
30A |
2A |
|
Forward Voltage Drop |
~1V |
~0.715V |
|
Reverse Leakage Current |
<5μA (microamperes) |
<25nA (nanoamperes) |
|
Reverse Recovery Time |
Not specified |
~4ns (nanoseconds) |
|
Speed |
Slow |
Fast |
|
Typical Applications |
Power supplies, rectification |
High-frequency circuits, signal processing, small-signal applications |
How to Choose between 1N4007 vs 1N4148
Choosing between the 1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes depends on the specific requirements of your electronic circuit. Here are some guidelines to help you decide:
Choose 1N4007 (Rectifier Diode) When:
- High Voltage: If your application involves high voltage levels (typically above 100V), the 1N4007 with its 1000V rating is the suitable choice.
- Higher Current: When dealing with higher current levels (typically above 200mA), the 1N4007's 1A rating is more appropriate.
- Power Supply or Rectification: If your circuit involves power supply design, rectification of AC to DC, or applications with substantial voltage and power requirements, the 1N4007 is the better option.
Choose 1N4148 (Small-Signal Diode) When:
- High-Frequency Applications: For high-frequency circuits and signal processing applications, the 1N4148's fast switching speed (quick recovery time) is advantageous.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: When minimizing voltage drop across the diode is crucial, such as in low-power circuits or when energy efficiency is a concern.
- Small-Signal Needs: In small-signal applications like amplifiers, oscillators, or protection diodes for sensitive components, the 1N4148 is a suitable choice.
- Low Voltage Applications: If your circuit operates at voltages below 100V, the 1N4148 with its 100V rating is adequate.
1N4007 and 1N4148 Datasheet
Check and download 1N4007 datasheet PDF>>
Check and download 1N4148 datasheet PDF>>
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between the 1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes hinges on the specific requirements of your electronic project. These diodes, although similar in appearance, have distinct voltage and current ratings that cater to different tasks. The 1N4007 is well-suited for high-voltage and moderate-speed applications, making it ideal for tasks like power supply rectification.
On the other hand, the 1N4148 excels in low-voltage and high-speed scenarios, making it a favorite for signal clamping and fast-switching applications. Always refer to datasheets and carefully analyze your circuit's needs to ensure you select the diode that best fits your project. Understanding the differences between the 1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes empowers you to make informed decisions and optimize the performance and reliability of your electronic designs.
 FAQ
FAQ
- Can I use 1N4148 diodes in low-power voltage clamping applications?
- Yes, 1N4148 diodes are often used in low-power voltage clamping applications to limit voltage levels and protect sensitive components from overvoltage conditions.
- Can I use 1N4007 diodes for flyback diode protection in relays and inductive loads?
- Yes, 1N4007 diodes are suitable for flyback diode protection in relay coils and inductive loads. They can prevent voltage spikes that occur when the coil is de-energized from damaging other components in the circuit.
- What is the reverse recovery time of 1N4007 and 1N4148 diodes?
- The reverse recovery time of a diode is the time it takes to switch off and stop conducting when the voltage across it changes from forward bias to reverse bias. 1N4007 diodes have a relatively longer reverse recovery time compared to 1N4148 diodes. The 1N4148 diode is known for its fast switching and low reverse recovery time.
- Can I use a 1N4007 diode in place of a 1N4148 diode, or vice versa?
- While you can technically use a 1N4007 diode in place of a 1N4148 diode, it may not be the most efficient or cost-effective choice for small-signal and high-frequency applications. The 1N4007 is overkill for such applications and may have slower switching characteristics. It's generally better to select the diode that matches the voltage and current requirements of your specific application.
1N4007-T In Stock: 6726
 Popular Industry Focus
Popular Industry Focus
Hot Products
-
AP331AWG-7
Diodes Inc
Comparator General Purpose CMOS, DTL, ECL, MOS, Open-Collector, TTL SOT-25
-

AP1661AP-G1
Diodes Inc
Power Factor Correction - PFC
-
AP2301AFGE-7
Diodes Inc
Power Switch/Driver 1:1 P-Channel 2A U-DFN3030-8 (Type E)
-

PI7C8150AND
Diodes Inc
PCI Bridge Chip 66MHz 256-Pin BGA
-
SBR8U60P5-13
Diodes Inc
Diode 60 V 8A Surface Mount PowerDI™ 5
-
PI7C8154BNAE
Diodes Inc
PCI-to-PCI Bridge Interface 304-PBGA (31x31)
Related Parts
-

DME2205-000
Skyworks Solutions, Inc
PIN Diodes Bands S and C Common Cathode
-

SMP1325-085LF
Skyworks Solutions, Inc
PIN Diodes .5 ohm @ 100mA .56pF max @ 20Volt
-

CD-MBL110S
Bourns Electronic Solutions
Bridge Rectifier Single Phase Standard 1 kV Surface Mount
-

RS406GL-BP
Micro Commercial Components
Bridge Rectifier Single Phase Standard 800 V Through Hole RS-4L
-

BAP51-02,315
NXP Semiconductor
RF Diode PIN - Single 60V 50 mA 715 mW SOD-523
-

JANTX1N5306-1
Microchip Technology, Inc
Current Regulator Diode 100V 2.42mA 500mW 2-Pin DO-7 Bag
-

BZV55-C8V2,115
Nexperia Semiconductor (NXP)
Voltage regulator diodes
-

KBPC5010W-G
Comchip Technology
Bridge Rectifier Single Phase Standard 1 kV Through Hole KBPC-W
-

SBR8U60P5-13
Diodes Inc
Diode 60 V 8A Surface Mount PowerDI™ 5
-

JAN1N5288UR-1
Microchip Technology, Inc
Current Regulator Diode 100V 0.429mA 500mW 2-Pin DO-213AB
-
BZX84C11LT1G
ON Semiconductor, LLC
Zener Diode 11 V 225 mW ±5% Surface Mount SOT-23-3 (TO-236)
-

CD-MBL106S
Bourns Electronic Solutions
Bridge Rectifier Single Phase Standard 600 V Surface Mount
-

RN141GT2R
ROHM Semiconductor
PIN Diodes 50V; 100mA PIN Diode
-

Z4GP210-HF
Comchip Technology
Bridge Rectifier Single Phase Standard 1 kV Surface Mount ABS(Z4)
-

MA4P7464F-1072T
MACOM Technology Solutions
PIN Diodes DIODE, PIN, MRI APPLICATION

 Update Time: Sep 15, 2023 Consumer Electronics
Update Time: Sep 15, 2023 Consumer Electronics