What are Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors?
 Published: Apr 27, 2023
Published: Apr 27, 2023
Contents
What is a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistor?

A negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor refers to the phenomenon and material of a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient, which decreases exponentially with the temperature rise.
NTC thermal semi-conducting ceramics are mostly spinel structures or other structures of oxide ceramics with negative temperature coefficients; the resistance value can be approximated as
R(T) = R(T0) * exp(Bn(1/T-1/T0))
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermistors
Advantages of Thermistors
1、Small size
2、Very high sensitivity (selection range)
3、Polarity insensitive
4、No cold-end compensation
5、A variety of sensor options
6、Cheap
7、Fast response
Disadvantages of Thermistor
1、high resistance, noise problems
2、Resistance and temperature characteristics are non-linear
3、Unstable due to drift and de-calibration (especially at high temperatures)
4、Thermistors are not suitable for use in a very wide operating range
Principle of NTC Thermistor
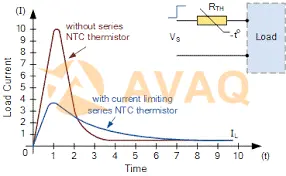
The NTC thermistor has a rated zero power resistance value, and when it is connected in series in the power supply circuit, it can effectively suppress the power-on inrush current. (And after the inrush current suppression is completed, the resistance value of the NTC thermistor drops by a very small amount using the continuous action of the current.)
What is an NTC Thermistor Used for?
Power-Type NTC Thermistors
They are mostly used for power supply surge suppression. The NTC thermistor for surge suppression is a high-powered, disc-type thermistor commonly used in electronic circuits with capacitors, heaters, and motor start-ups.
At the moment the circuit power is turned on, the circuit generates an inrush current many times higher than normal operation, and the NTC thermistor has a large initial resistance value, which can suppress the excessive current in the circuit, thus protecting its power circuit and load.
When the circuit enters normal operation, the temperature of the thermistor body rises due to the passage of current, and the resistance value drops to a very small value.
Text for Thermistor
When applying a thermistor, several of its more important parameters must be tested.
In general, thermistors are highly sensitive to temperature, so it is not advisable to use a meter to measure its resistance value. When operating current of the multimeter is relatively high, flowing through the thermistor will heat up and make the resistance value change. However, the multimeter can also be used to easily determine whether the thermistor can work, the specific thermistor detection method is as follows:
Dial the multimeter to the ohmic block (depending on the nominal resistance value to determine the block), with an alligator clip instead of a pen to clamp the thermistor's two pins, respectively, to note down the resistance value at this time; then pinch the thermistor with your hand, observe the multimeter, you will see the data displayed (the pointer will slowly move) as the temperature rises and changes, which indicates that the resistance value is gradually changing (negative temperature coefficient thermistor resistance value will become smaller) This indicates that the resistance value is gradually changing (negative temperature coefficient thermistor resistance will become smaller, while positive temperature coefficient thermistor resistance will become larger).
When the resistance value changes to a certain value, the display data will (pointer) gradually stabilize. If the ambient temperature is close to the body temperature, then this method will not work. In this case, a soldering iron or a cup of boiling water can be used to heat the thermistor near or close to the thermistor, and the same resistance value will be seen to change.
In this way, the temperature coefficient thermistor can be proved to be good.
When testing a negative temperature coefficient thermistor with a multimeter, noting that the nominal resistance on the thermistor is not necessarily equal to the multimeter reading is important for you. This is due to the fact that the nominal resistance value is measured at 25°C with a special instrument.
When measuring with a multimeter, a certain amount of current is passed through the thermistor and heat is generated, and the ambient temperature is not necessarily 25°C, so errors will inevitably occur.
 Popular Industry Focus
Popular Industry Focus
Hot Products
-
![ASMB-MTB1-0A3A2]()
ASMB-MTB1-0A3A2
Broadcom Limited
Standard LEDs - SMD PLCC4T MtBS WF Silicone RGB
-
![TLP785(GR-TP6,F)]()
TLP785(GR-TP6,F)
Toshiba
It operates at a maximum input current of 8mA and offers a high isolation voltage of 5kV
-
![LTC5549IUDB#TRMPBF]()
LTC5549IUDB#TRMPBF
Analog Devices Inc.
2GHz to 14GHz Microwave Mixer with Integrated LO Frequency Doubler
-
![KSC5026MOS]()
KSC5026MOS
onsemi
NPN Silicon Transistor
-
![PCI9056-BA66BI G]()
PCI9056-BA66BI G
Broadcom Limited
PCI Interface IC 32-bit 66MHz PCI BUS Mastering I/O
-
![TLP521-4GB]()
TLP521-4GB
Isocom Components
Optoisolator Transistor Output 5300Vrms 4 Channel 16-DIP


 Update Time: Apr 27, 2023 Consumer Electronics
Update Time: Apr 27, 2023 Consumer Electronics